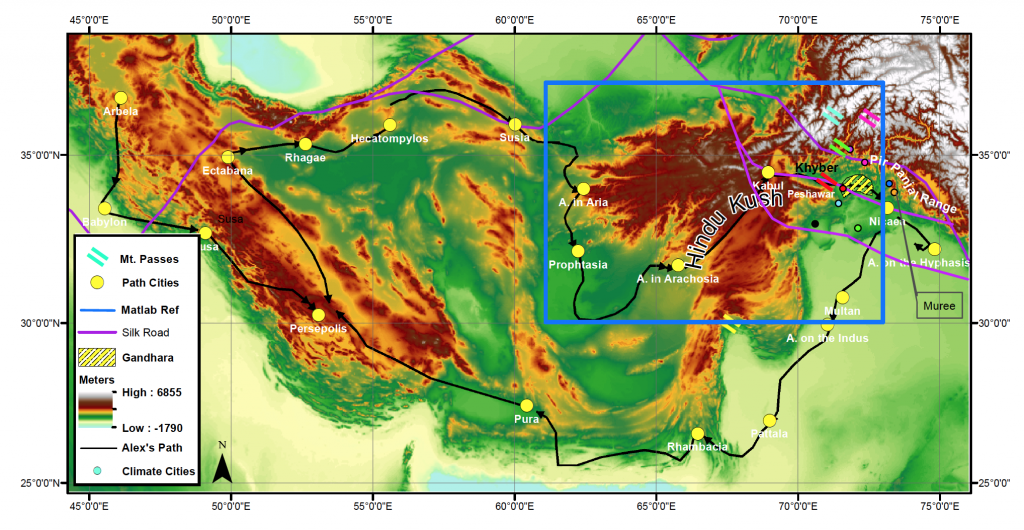
Around this time last fall, I was spending consistent hours in the basement of Fine Hall, gathering data from the Map Library and struggling with ArcGIS and Matlab to make sense of it. My goal? To explain the success of Gandhara, a little-known ancient civilization in northwest Pakistan.
I first learned about the region during an independent research project in my last semester of high school Latin. Gandhara started as an outpost for Alexander the Great’s generals but grew into an incredible region of diffusion between Greek and Indian cultures. Greek and Buddhist influences merged freely in philosophy, religion, and art, and not much research existed on the area.
Gandhara slipped from my mind until I resumed school in my first semester at Princeton. I was enrolled in FRS 187: Earth’s Environments and Ancient Civilizations, a geoscience seminar that traveled to Cyprus over fall break. In Cyprus, we used geophysics to examine unexcavated areas near a Princeton archeological dig house. As part of the course, we were responsible for writing three scientific papers explaining why a civilization succeeded or failed using topographical, mineral, and climate-based evidence. My mind turned naturally to Gandhara. I wanted to create one comprehensive paper examining its success, but I wasn’t sure that I could find sufficient evidence from three different angles.
Continue reading All Roads Lead to Gandhara: Integrating Science and the Classics

