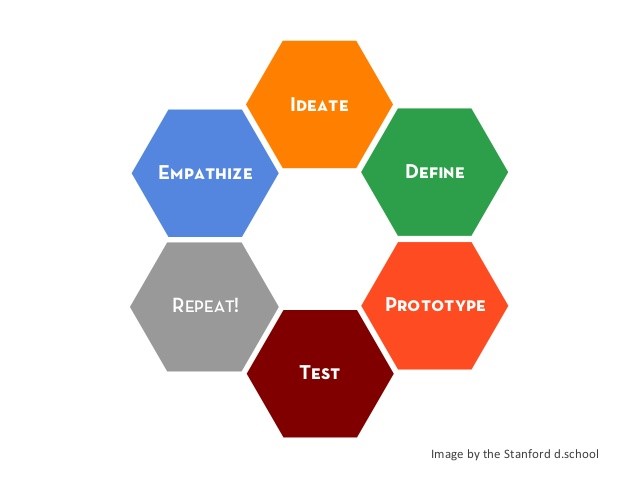
When we think of academic research, we often think of libraries or labs. We might imagine flipping through books, reading articles, or running lab experiments, but there is a branch of research that looks much different than this. In fact, it looks like the real world.
This branch is field research. Researchers from various fields apply this method of research, but in this post, I’ll be focusing on field research in design. Design is a big field with a wild range of applications. Design spans from information design (think infographics, instructions, maps) all the way to User Interface design (think apps and websites), but what’s at the root of design is a need to communicate effectively with people and facilitate understanding. The goal in design is to create systems that are effective–ones that work for their users. Accordingly, when designers conduct field research, they go out in the world and record qualitative data on people’s needs and experiences: What information are they searching for? What do they want out of a product? What parts of the current product are helpful? Which are frustrating and confusing?
In this interview, Sheila Pontis, a lecturer in the Keller Center, talks about her work and encourages designers and student researchers to embrace field research and trust qualitative data.
Continue reading Trust the Qualitative: An interview with Sheila Pontis about Field Research