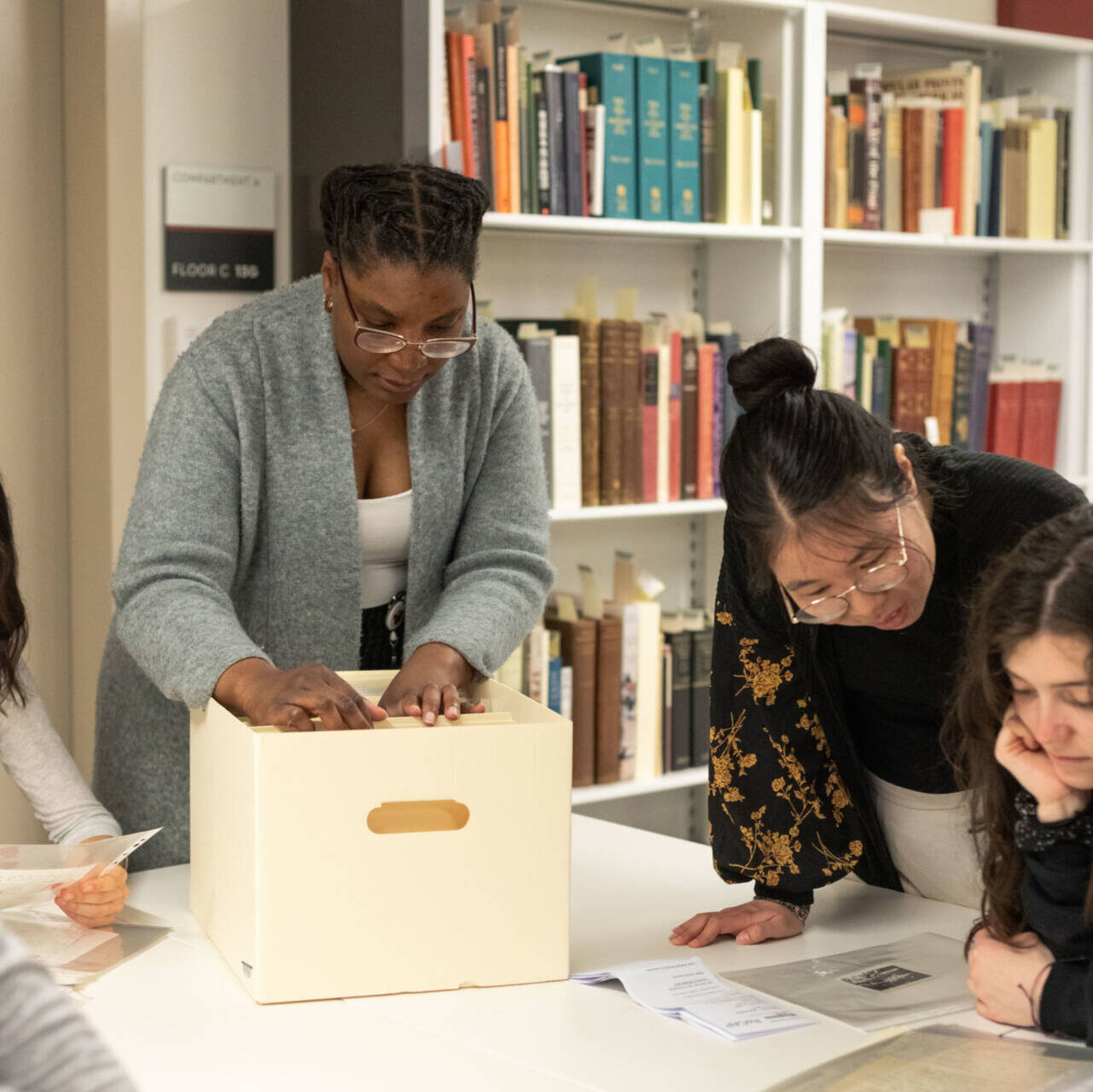
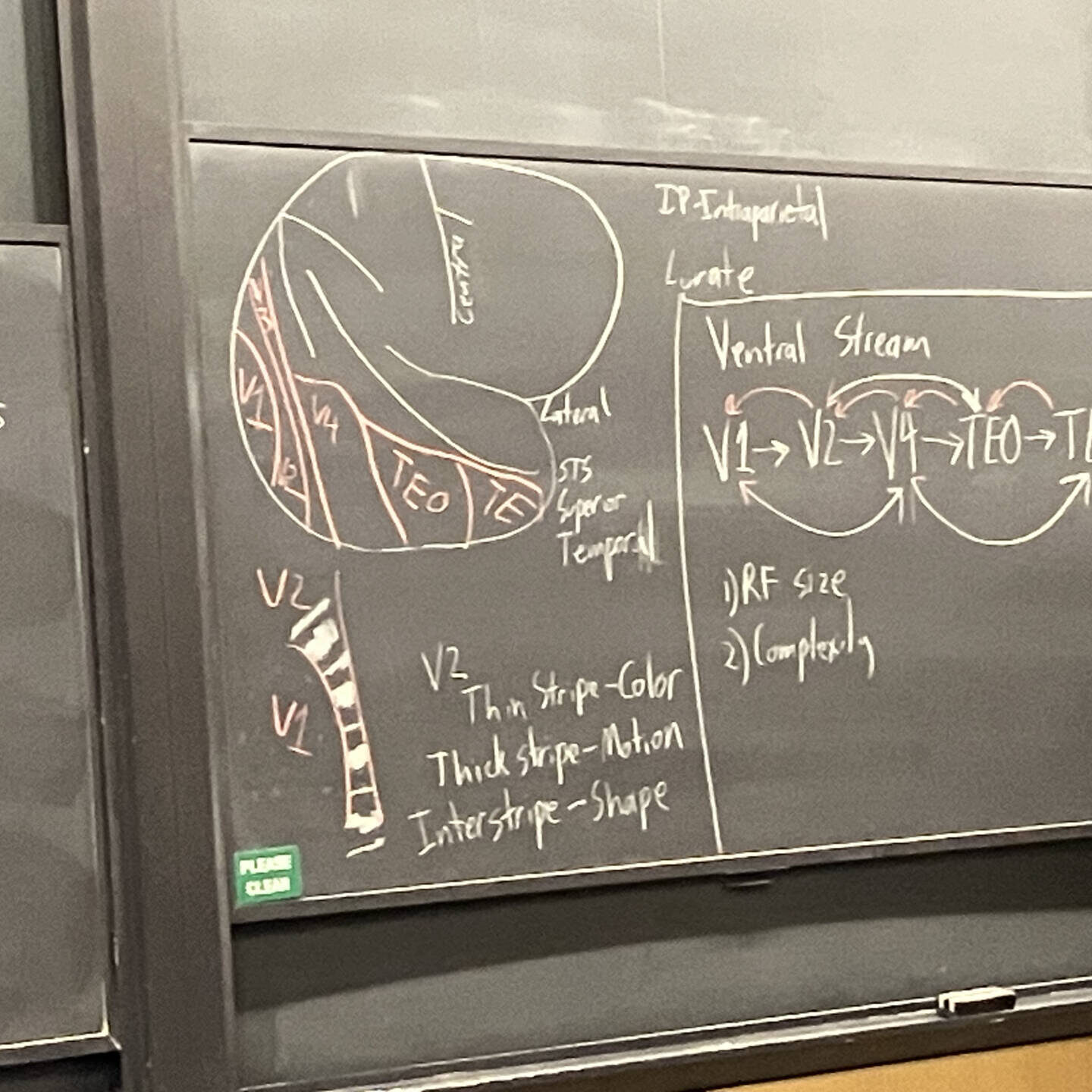
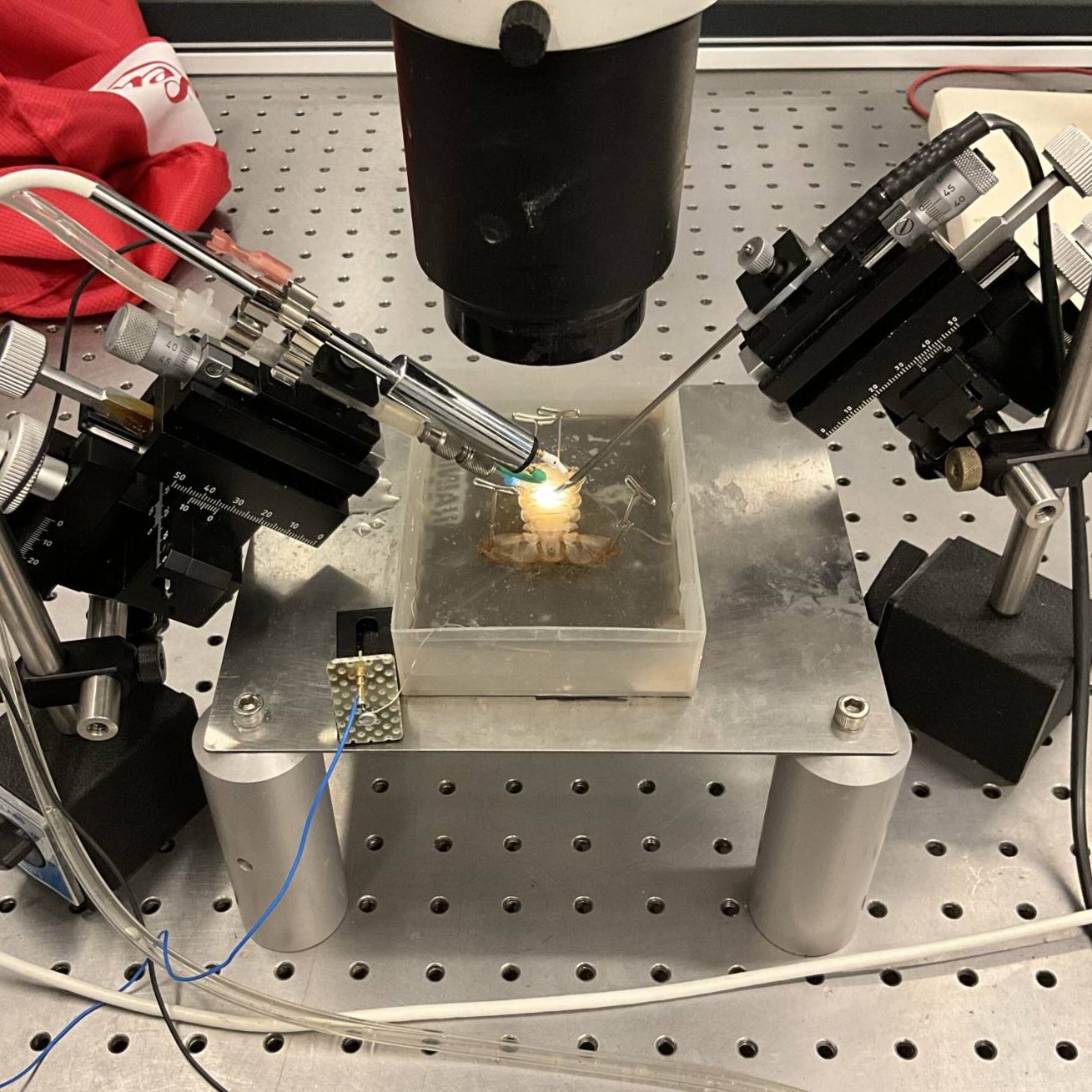
Many STEM majors here have the same rite of passage: core lab. For non-lab majors, core lab is a class that is purely to teach you about lab techniques and critical thinking skills that are useful for writing our theses. They usually involve a bit of a simulated lab experience where you discover new findings while the teachers guide you through the motions of a lab research experience.
Molecular biology’s core lab meets twice a week for 3 hours and then a small 50 minute lecture/precept on Fridays for half the semester. Other majors have similar constraints. However, while at first it may seem a bit overwhelming and even redundant if you’ve already done these procedures in a lab or are in a lab that definitely will not be using any procedures you learn, core lab goes beyond just teaching you technical skills.
I too was confused as to why I was here and why this mattered, but over time, I began to internalize one of the real skills this class is meant to teach you, something that pipetting will never give you: asking the right questions.
Continue reading In Defense of Core Lab